Obesity is perhaps the biggest single health problem in the middle and high income groups all over the world, but more prevalent in civilised people. They are often subjects of pity and ridicule rather than respect. In most cases people realise about their obese condition too late and is not a sign of property, nobility amiability and economic stability as considered by lay public.
Obese persons are sometimes happy with their sociable nature and impressive personalities, but it is a more serious condition as it is associated with an increased tendency of development of more dreadful consequences of different chronic diseases. It is not only a medical risk factor but also a serious social, psychological and economic problem.
What is Obesity?
The term obesity, a latin word, means “to eat away” or “to devour” which denotes over eating seems to be the basic fault.
- The medical dictionary definition of obesity describes it as “a bodily condition marked by excessive general deposition and storage of fat.” Obesity and over weight are not synonymous. Over weight is an excess of fat accumulation causing over heaviness in the body where the body weighs about 10 to 15% than normal good weight.
- It is also defined as any degree of excess adiposity that imparts a health risk.
- It can also be defined as adiposity (collection of fats) in excess of that consistent with good health.
Medically, it is a self generated benign-unrecognised chronic disease of metabolism. Obesity is a condition of the body characterised by over accumulation of fat under the skin and around certain internal organs, where the body weighs more than the ideal weight by 20% or more.
How to measure the body fat? What constitutes the body weight?
Body weight is made up of several components and those such as fat, muscles and bone, which vary according to age, sex and height .
What is the standard weight?
A standard weight is based on height, bone, structure, sex and also varies from small frame to large frame from men and women aged 25 yrs and above.
Standard weight chart for Indian male & females
IDEAL HEIGHT WEIGHT CHART FOR INDIAN ‘MEN’
(Weight in Kilograms)
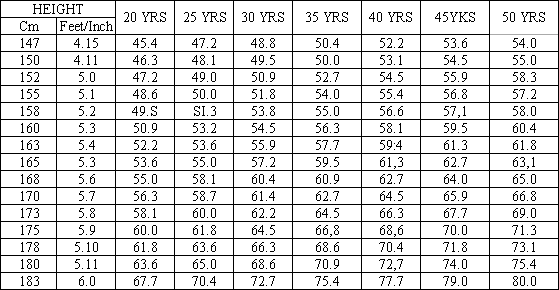
IDEAL HEIGHT WEIGHT CHART FOR INDIAN ‘WOMEN’
(Weight in Kilograms)
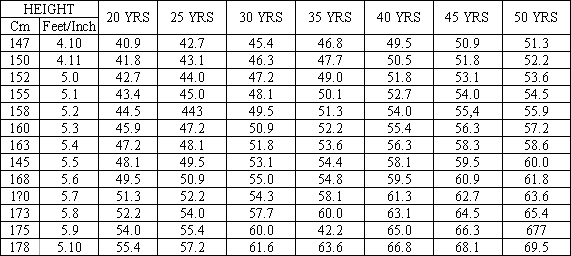
How to ascertain the presence of excess fat?
1. First Method: If a person gets breathless even at the slight exertion or feels tired after climbing a stair case, he should take it as an indication of the presence of excess of fat in the body.
2. Second Method: Mirror also supplies reliable evidence of excess fat accumulation. Generally fat accumulates on the chin, neck and the belly and the waist of men and on the breasts, the belly, the waist, the thighs and the buttocks of the women.
When a person wearing only underwear stands before a mirror, he can observe of these portions of the body whether there is excess of fat or not.
3. Pinch test or Skin fold test: In this method pinching
- At a point midway between your shoulder and elbow measured while arm is hanging loosely between thumb and fore finger, or specially designed callipers.
- Pinch a little flesh over the lower two or three ribs under the arm pit. If a pinch is more than one inch, it will denote extra fat or obesity.
4. Eye ball test: Stand erect. Sink your chin into your chest, look down, you must be able to see your toes without a turtle like extension of the head. If not you are obese.
What determines the degree of obesity?
With reference to a standard weight chart if your are more than
- 1. Ideal weight + 20% extra weight, you are clinically obese.
- 2. Ideal weight + 40% extra weight, you are said to have gross obesity.
- 3. There’s also another precise means. Take a tape and measure your chest and then your waist. In case of women, chest is measured beneath breasts. The circumference of the chest should be at least four to six inches greater than the waist. If not, one is obese, carrying extra fat.
New methods of measuring body fat
- a. Hydro densitometry: a method where by body fat is measured under water, it sets the standard for accuracy but involves complicated formulas and highly trained technicians and laboratory equipments, which are expensive.
- b. DEXA (Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry).
- c. Bioelectric Impedance Analysis (BIA): In which a small electrical current is sent through the body to measure, the impedance or resistance, biological tissues such as muscle, fat, bone, connective tissue, act either conductors or insulators to the current. Generally, current flow through the path of least resistance, muscle tissue acts as a good conductor as it contains about 80% water, while fat contains very little water acts as an insulator. In this the resistance value to the current by fat tissue is measured and inserted into an equation (along with height, weight, sex, physical stature) which calculates body density and percentage of fat to high level of accuracy.
Types of Obesity
I. According to the distribution of fat it is of two types.
- Localized: When it is, localized mainly in the abdomen it is called is android as male pattern and when localizes in hip region it is Gynoid or female pattern (Pear Shaped).
- Generalized: In this fat is distributed all over the body without localized condition.
II. According to the severity it is classified as
- Mild Obesity
- Moderate Obesity
- Severe Obesity
III. According to the causative factors it is classified as :-
- a. Exogenous Obesity.
- b. Endogenous Obesity.
a. Exogenous Obesity: Factors include
1. Over eating: Excess intake of food leads to excess calories, as large percentage of obese eat to serve their moods. Food is misused as tranquihzer and as a safety valve for pent up feelings. Excessive calorie intake than required leads to accumulation of body fat as the body does not need them for maintaining body heat and other functions.
2. Food Habits and Cultural factors: Eating of fat rich diet, refined foods, sugar and sweets, alcohol intake, frequent eating habits, non-vegetarian foods, eating processed and tinned food, aerated drinks, excess intake of coffee, tea, fried food, ice creams, chocolates, pastries, etc. If the food assimilated is not oxidised, it accumulates as fat in adipose tissue. Cultural factors also play important role to eat heavily rich food for many executive professionals and businessmen as progressive modernisation led to many changes in the modes of living and eating of denatured, de-vitaminized and de-mineralized food, which contributes a serious deficiency of B vitamin groups particularly which play vital part in the oxidation of nutrients in the cells and release of energy. Net result is slowing down of metabolic process leading to an imbalance between food consumption and expenditure, which in turn leads to obesity.
3. Disturbance in body metabolism (energy intake and energy output): The rate of metabolism is different with different people. It mainly depends upon the habits of living, nature of activeness and psychological factors. It is of in three ways.:
- The body forms fat ajt a rate that is faster than normal.
- The body stores fat at a rate that is faster than normal.
- The body disposes off stored fat at a rate that is slower than normal. The disturbances work in these three ways and all are very damaging. However the question whether it is obesity that causes metabolism disorder or is it the metabolic disorder has been a great challenge for the modern science.
4. Physical inactivity or sedentary life style: It may be due to
- Sedentary nature of work
- Exercise avoiding attitude, lethargy, lack of consciousness of health.
- Habit of taking excessive rest and sleeping.Interested more in watching television programmes.
- It may be enforced as in post-operative rest.
- Old age with chronic ill health and general debility.
5. Psychological and Social factors : In modern society many people eat not to satisfy their hunger but to enjoy and relish tasty dishes. In creating such situation the contribution of advertisements of processed foods through mass media is by no means small. Many people try to find an easy solution to serious problems and tensions of life through food. Sense of insecurity, depression and failures, loss of loved family members in accidents or death by any cause generates a tendency to eat more and more. In some people, anxiety, worry, depression, love failures divorce, loneliness, unmarried, married too late due to financial and other causes, unsuccessful in business, non-cooperation from office colleagues or higher officials leads to emotional excitement, alcoholism, inactivity or moody mentality and causes over eating mostly unnatural and tasty food to satisfy their moods.
It is also present in childless couples and also people who have spent their childhood in poverty and gaining wealth in due course, tend to eat more. These persons are called self made men.
Fat people generally present their obesity as an excuse to over their failures and laziness and make convenient excuse to avoid responsibilities. However mental tensions does not always lead to obesity and in some cases causes reverse.
In short, psychological factors do play an important role in causing obesity.
b. Endogenous Obesity:
o Heredity: Whether genetic factors do play a role in causing obesity is still having contradictory opinions. However, most of the experts hold the view that genetic factors have role to some extent. It is undeniable fact that generally the children of fat persons are also fat as every individual inherits his physical constitution and it is closely associated with the obesity. Heredity seems to be particularly influential in where fat settles in the body and number of fat cells.
Generally adults have anywhere from 30 billion to 40 billion fat or adipose cells. They swell or shrink like sponges with the amount of fat inside them. Number of fat cells may be hereditary.
The main reason why it seems to run in certain family is the fact that members of the family not only inherit certain traits but live together, eat together and cultivate more or less same habits of eating and living.
o Endocrine Disroders: Endocrine glands secrete hormones. The glands which are associated with obesity are pituitary, which is located at the base of the brain, the thyroid gland, which is located in the front of and on either side of the wind pipe. The adrenals, two small glands located above each kidney, the pancreas lying behind the stomach and sex glands , the ovaries, in females and the testes, in the males.
The secretions of these glands perform specific functions in the body. Some of these functions relate to obesity.
However, most obese people have no pituitary disturbance under secretion of thyroid gland called as Hypothyroidism leads to low body metabolism and leads to deposition of excess fat in some people.
Pancreas : the main function is to secrete insulin, a substance which is vital in Glucose metabolism and control of fat formation. Insulin speeds up the body’s transformation of carbohydrate into fat and also works on the storing of the fat and inhibits the release of fat already stored for energy. Obese people generally tend to have an over responsive pancreas gland and produce excessive quantities of insulin. When they eat a certain amount of carbohydrate they get a higher rise in insulin than a non obese person leading to formation and storage of fat in the body.
Adrenal gland: Over active adrenal glands cause a disease called Cushing’s syndrome which creates a unique pattern of fat deposit , puts on excessive fat over spine, the upper chest, the hips and most notably the cheeks. However this disease is rare. But, when certain people are under stress or tension, their system, puts out more secretion of adrenal gland called hydrocortisone, which tends to increase appetite and feels better when they eat more causing indulgence of food which results obesity. Lack of sex hormones is also related to obesity and has some role to play particularly in governing the distribution of fat in a small minority of obesity cases. However, obesity leads to imbalance in sex hormonal ratio resulting increase in the levels of testosterone (the male hormone) in blood leads to hirsuitism (excessive hairs on face arms and legs) and also ovulatory disturbances such as irregular periods and infertility.
In obese men it hampers sperm production and in women polycystic oyary disease also causes obesity weight gain in women following menopause is not uncommon. However in these cases obesity is secondary to the diseases proper.
o Iatrogenic obesity:
a. Hypothalamic surgery.
b. Intake of certain drugs like contraceptive pills, cortisone group of drugs, powerful antibiotics disturb the delicate balance of the hormonal system, which regulates fat metabolism causing water retention in the body and triggers fat production and accumulation.
c. Over care after surgery and during pregnancy: Even for a minor surgery self prescribed bed rest for long period, over eating of food, use of tonics result in obesity.
During pregnancy and after delivery: over eating, lack of exercise and more rest leads to increase of weight.
d. Sleeping more time immediately after food in the day as in old age, disease, pregnancy, stress and other conditions leads to increase in weight.
Complications of Obesity
Leaving aside the cosmetic importance of being obese, it is the commonest predisposing cause for the following complications.
Medical Complications
1. Hypertension: Generally, blood pressure tends to go up as weight increases. Research has shown that there is increase of blood pressure steadily in proportion to the body weight. Obese people have high blood pressure probably because the extra fat puts a special burden on the circulatory system as there is more tissue for the blood to reach. Due to high cholesterol in obesity, there is chance of atherosclerosis causing hypertension. Obese people are more prone to thrombo-phlebitis and varicose veins.
2. Coronary Artery Diseases: Obese person with high blood pressure experiences a greater risk of coronary heart disease and heart attacks than non-obese person with high blood pressure. Death rates of obese persons with high blood pressure are higher than those of non-obese.
3. Diabetes (Type II-NIDDM): Research has shown that 95% of the diabetes in our country belongs to non-insulin dependent and that eight out of ten persons of type II are obese. Diabetes is often described as ‘fat man’s folly’ is a reasonable name. If the weight loss is maintained by right way of living, diet and exercises, obesity related diabetes is indeed controllable and curable.
4. Gall Bladder Stone Formation: Generally, obesity leads to high proportion of cholesterol in the blood, which causes stone formation in the gall bladder.
5. Digestive disorders: The liver is also adversely affected by obesity. It has been found that degenerative diseases of liver and cirrhosis of liver are more common in obese people. Obese persons are found to be suffering from intestinal diseases like diverticular disease of the colon, external and internal piles, constipation, gas formation, etc.
6. Cancer: Research studies of the natural institute of health, Baltimore City hospital, LJ.S.A have shown that obese men have higher incidence of certain cancers including those of large intestine, rectum and prostate. Obese women run a greater risk of cancer of ovaries, uterus and after menopause to the breasts.
7. Complications While Undergoing Surgery: During surgery surgeons job becomes more difficult as he has to cut through thick layers of fat, but the real problem is that during anaesthesia, strain increases on breathing which has been proved to be fatal in many cases of obesity.
8. Respiratory Difficulties : One has to breath to live. For a obese person breathing is difficult because excessive weight causes to carry an extra load on the chest wall and abdomen. When breathing decreases less oxygen is taken into the blood and more carbon dioxide builds up. When it happens, the person becomes sluggish and lethargic. Lack of oxygen in the blood of arteries causes increase in the number of blood cells leading to the danger of thrombosis or blood clot, which may lead to heart attack and death.
Bronchitis is also common in obese people.
1. Reproductive System: Obesity adversely affects the nerves and endocrine glands and the married life often becomes a tragic tale. Obese women suffer form menorrhagia, infertility and several other disorders of menstruation. It also causes many problems during pregnancy such as toxemia, difficulties during delivery, post delivery bleeding, still births and abortions etc. In most cases, obese women need caesarean delivery.
2. Endocrine Glands: Obesity disrupts the functioning of endocrine glands of thyroid, ovaries, adrenal glands and mostly pancreas causing different diseases. Diabetes is a common complaint in obesity.
3. Muscles: Muscles of a fat person are generally soft and weak as they are not engaged in any physical activity. Due to low muscle tone fat persons are slow in their reflex actions and as a result they are more prone to accidents and injuries. They feel breathless after slightest physical exertion, therefore, they become lazy, inactive and slow. If the muscles are weak, they cannot support the internal organs of the body and easily get displaced organs causing different types of hernias and particularly incisional hernia after operation.
4. Excretory System: Degenerative changes in the kidneys occur more severely and early in obese persons. Fat persons sweat profusely as fat person spend lot of energy to do any physical work and also the layers of fat deposited under the skin acts as woollen jackets and causes profuse perspiration. Sweat of a fat person often is of foul smelling, heat rashes are common in obesity. It also makes skin early wrinkling, stretch marks, premature greying and ageing. Skin diseases are common in the skin folds between buttocks, between scrotum and thighs, below breasts and arm pits in women. Stretch marks, heat rashes are also common in obese people.
B. Mechanical Disabilities: Osteoarthritis of knees is common in obese people due to weak ligaments and extra weight bearing condition, low back ache and lumbar spondyiosis due to protruded abdomen with fat causing strain on back muscles of the spine. Flat feet are also common in obesity.
C. Psychological Disturbances: This is an important and sensitive complication of obesity. Fat people have low self esteem, usually with low confidence and inferiority complex, which will naturally have impact on their work.
D. Life Expectancy: Extra amount of fat which has no vital function also needs blood circulation and more blood vessels carrying the blood to draw away from the vital organs thus weakening them and starving them of nourishment and oxygen. Loading them with toxins which are not eliminated and predisposing them to a variety of diseases. Generally, obese people have short life and age faster than those who are comparatively lean.
Natural Methods for Weight Reduction
Naturopathy treatment for obesity should be taken as per the advise and continuous supervision of an expert Naturopath.
Now a days, obesity is a big business as it is a problem of mainly affluent people having plenty of money to spend. Many health clubs are advertising weight reduction regimens catching hold of the weakness of a customer and repeatedly advertise saying “No dieting, no exercise and no gadgets” etc. Having paid huge sum in advance, the person invariably follows what the club says and they are put on restricted diet and on so called diet supplements and the weight reduction problem will be same with little result. The diet supplements do not help for normal functioning of the body. Without natural balanced nutrition, all appetite killers, sedatives, diuretics, hormones, laxatives, and certain other drugs to increase metabolism are highly dangerous with undesirable side effects.
Obese people should understand the following points.
1. Obese people should not be confined to overcoming only to get rid of unwanted fat. Firstly, obesity is an unhealthy condition. Secondly, this condition is the result of years of wrong living and eating right from childhood or any time. Thirdly, this unhealthy condition makes you prone or predisposed to a host of serious diseased conditions afflicting various vital organs of the body.
2. The secret of success is discipline, not discipline imposed from outside but self discipline which is cultivated and strengthened by will power.
3. Losing weight requires changing long standing habits. It needs continuous effort and motivation. If you are not really motivated, you shall keep looking weight and gaining back and that is not healthy.
4. Find Right Reasons: Any programme or project starts with a commitment. Most people often make a commitment to weight loss not because they wanted to but because they are told to by their doctors or their families or by comments of colleagues, try to lose weight because others want you to look slim. These causes may keep you motivated for a few weeks only. Keep in mind that you are losing weight for your health and fitness but not for others.
5. Set Realistic Goals: Another reason many people find it hard to maintain weight loss is that they set their mind for losing say 20 kgs and when they find out that it requires too great sacrifice, they give up the effort, blaming themselves or their genes and other reasons. Have a realistic goal in mind. Positive mental attitude is very essential for achieving the goals and weight management. Fix for your self a modest goal in the beginning so that you will be able to keep up your resolve and steadily strengthen your will power. If you remain steadfast it should not be difficult to advance closer and closer to the ideal goal. By this you feel more active, more agile and more energetic progressing towards health and predispositions to other conditions vanish automatically.
6. What actually needed is a comprehensive programme, which include a1 sensible course of dieting, fasting, exercise, plenty of fresh air, sunshine, combining some water treatments, massage etc to eliminate the unwanted toxic condition from the system. It will be a programme to improve holistic health for physical and mental fitness. Even Naturopath can give only some guidance only regarding these factors. It is for you to decide how you will approach the ideal.
Depending on the severity of obesity the diet, exercise and treatment regimen can be planned. If one has to lose only 10 to 15 kgs, he can manage at home with a will power. In severe obesity, it is advisable to get admitted in Nature Cure Hospital, under the guidance of experts to lose substantial weight in 4 to 8 weeks time, so that remaining unwanted weight can be shed at time.
One should understand thoroughly that some degree of dietary restriction with regular exercise will be necessary permanently even after ideal weight is attained. Weight loss should be gradual and does not expect 4 to 6 kgs initially in a month. It is very important to build health at the same time.
